Fungal diseases are a fairly widespread phenomenon. But not everyone understands exactly how such problems should be treated. Often, people buy medicines at the pharmacy "recommended by a neighbor" or try to cope with traditional medicine. Some people with this approach to treatment suffer from their problem for years.
But in order to effectively and quickly defeat the fungus, you need a specialist consultation and properly selected drug therapy. After completing the necessary tests, the specialist will be able to prescribe a medicine that will help overcome the hated problem. Often, the destruction of the fungus requires procedural local treatment, in which the affected tissue is cleaned and the source of infection is neutralized. The most important thing is to know that independent treatment methods are not effective. Let's figure out exactly how to choose the right treatment.
This article is not a guide for independent drug selection, but only provides you with a better understanding on the basis of which the dermatologist makes decisions. All situations are individual and it is easy to ignore contraindications and important nuances of the course of the disease, which the doctor will certainly notice and take into account when choosing antifungal therapy and the duration of treatment.
What is fungus or mycosis?
Mycosis, which is popularly called fungus, is a series of highly contagious infectious diseases.
- Pathogenic: parasitic fungi of various types (pathogenic and opportunistic).
- Affected area: skin, nails, hair, mucous membranes.
- Relapses: very likely.
Where you can catch it: Public places like baths, showers, gyms, swimming pools, beaches and more.
How the infection occurs: contact with the mucous membrane, microcracks on the skin.
The disease is highly contagious. It is almost impossible to fully recover on your own. Mycoses are most dangerous for people with reduced immunity, when their general condition is worse than normal. The help of a doctor and the right choice of antifungal drugs can solve the problem.
You can get infected from someone else's cat or by contact with objects on which fungal infections have left spores. But not all types of fungal infections are pathogenic. There are also species that are normally constantly present in the body, and in some cases are even beneficial (for example, Candida). But if the fungal growth has increased, treatment may be necessary.
Causes of mycosis
A healthy person with good immunity usually does not suffer from pathogenic fungi. If everything is in order with the immune system, then it can easily cope with such a load, and fungal development does not occur.
Decreased immunity
If your immune system is weakened, the risk of infection increases. If you have recently undergone antibiotic therapy, then your immunity is always reduced and you should be careful.
People with immunodeficiencies, cancer patients and patients undergoing cytostatic therapy are at constant risk.
Insufficient hygienic use of public places
- If a person visits a swimming pool or public bath, then it is always necessary to have a personal towel and flip flops with them.
- The same should be done when visiting the gym.
- It is recommended to try on shoes in the store with socks only.
- It is necessary to ensure that the professionals in the salons do not forget to sterilize the instruments.
- You may not use other people's toiletries.
- Wearing tight shoes or synthetic underwear is not recommended.
- If the skin is damaged, do not forget about antiseptics, because the infection occurs through damaged areas.
Chronic diseases
They themselves can reduce immunity and negatively affect the body's resistance. Skin diseases are particularly prone to problems such as fungal diseases: cracks, blisters. In some diseases, the skin becomes dry and brittle (in patients with diabetes, varicose veins). All dermatological diseases put a person at risk.
Personal characteristics
There may be personal characteristics that create favorable conditions for fungal diseases. For example, hyperhidrosis or sweating of the palms and soles. There are other individual characteristics that create a good environment for various types of pathogenic fungi.
Types of mushrooms
There is no classification that describes pathogenic fungi. Diseases are usually classified according to symptoms and degree of spread. Diseases such as nail fungus, skin fungus and foot fungus are classified as superficial mycoses. The prevalence of mycosis can vary:
- karatomicosis - when the microorganism is present only in the stratum corneum of the skin;
- dermatomycosis - if the fungal infection managed to penetrate the epidermis, hair follicles and dermis;
- candidiasis – damage to the mucous membrane.
There are also systemic mycoses, which are characterized by damage not only to the external integument, but also to internal organs.
Types of pathogens:
- Yeasts are normally part of the microflora.
- Molds are pathogenic.
- Dodmiphores are pathogenic.
In order to accurately determine the cause of the infection, and then prescribe an effective treatment based on special means, it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis. If the integumentary tissue is affected, a swab or scraping is taken. When the problem is with internal organs, the type of pathogen can be determined by microscopic examination based on blood analysis. Some types of lesions from infections have the same clinical signs, and the exact cause can only be determined by analysis.
How to recognize fungal disease - symptoms
Despite the fact that each type of infection has its own characteristics, which are manifested in different stages of the disease, superficial mycoses also have common signs of the disease:
- change in skin color - redness or loss of color;
- the appearance of constant peeling or weeping areas;
- itching;
- crusts.
For scalp damage:
- a sign of fungus is often dandruff;
- brittleness and hair loss.
on the face:
- appearance of damage in the crease of the upper eyelid.
on the feet:
- cracks;
- burning;
- bubbles;
- unpleasant odor is more common;
- skin roughness;
- thickening of the skin;
- ulcers (if there are also bacterial infectious diseases).
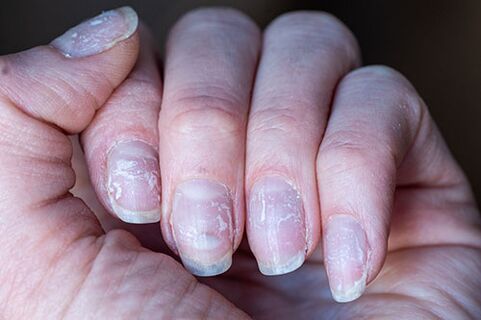
on nails:
- small white spots on plate;
- the affected nail has white streaks;
- change in color to black, yellow, brown;
- change in structure (becomes layered);
- nails become thicker or thinner;
- the nail plates move away from the bed;
- inflamed nail folds;
- changes in the shape or relief of the nail.
At first, the infection develops imperceptibly, and many people notice nail fungus only at an advanced stage of disease progression, and not when the condition of the skin and nails can be relatively easily and quickly corrected. If the first signs of pathological changes appear, an urgent consultation with a specialist is recommended.
Medicines for the treatment of fungi
Medicines for the treatment of fungi are called antifungals, from the words "anti" and mycosis, but are more often called simply antifungals. Such drugs are divided into two types based on their action:
- drugs for the treatment of fungi that destroy spores - fungicides;
- those that do not suppress the development and prevent the growth of a fungal infection, but do not destroy it, are fungistatic.
The type of therapy a doctor decides to prescribe is influenced by various factors, including the characteristics of the patient's body.
The potency of a particular drug varies depending on the following factors:
- dose of active substance;
- spectrum of action of the active substance.
Most often, fungi are treated with topical medications such as antifungal ointments. Oral drugs (antifungal tablets) are used if the fungus cannot be cured by external application or when the disease is of a systemic nature and has a long-term course. When the situation is very severe, even injections can be used to cure the fungus.
Release forms
Topical antifungals are produced in different forms:
- fats;
- creams;
- sprays;
- solutions;
- antifungal varnish (for nail lesions).
If the lesion is only external, then local therapy is sufficient. A characteristic feature of such drugs is that they have almost no side effects, unlike drugs for internal use. Complex therapy with the use of systemic antimycotics is prescribed for a more complex course of the disease, if there are relapses of the disease. Then therapy courses are possible. It is not always possible to correctly determine treatment methods based on clinical manifestations, so tests are needed. Sometimes fungal diseases intensify the course of allergic diseases from which the patient may fall ill. In that case, sorbents can be prescribed.
One of the most common substances for antifungal therapy is fluconazole. It is used for external and internal lesions. The substance is found in various medicines. Available in tablets, capsules, injections and other forms. To prevent fungi, antiseptic agents are used for the skin of the feet, palms and nails. Prevention also involves timely intake of vitamins to support the immune system.























